領 域 名 応用生命科学
教員氏名 木村義雄
研究分野 微生物生理学

研究キーワード:粘液細菌, シグナル物質, ATP合成,新規微生物資源

最近の研究課題
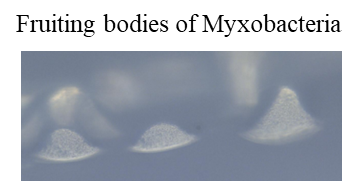
1.粘液細菌のシグナル物質について
生物は環境の変化が起こるとシグナル物質を生産して、環境の変化に適応するようになる。しかし、細菌における普遍的なシグナル物質としてはアミノ酸飢餓時に作られるppGppしか認知されていない。
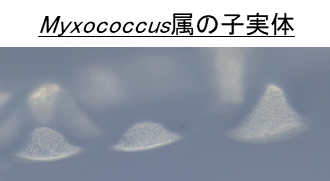
そこで生物全般においてアミノ酸飢餓時に作られるアデノシンポリリン酸(ApnA:n=3-6)と数十から数千のリン酸が重合したポリリン酸が、粘液細菌のどのような酵素によって合成及び分解されるのかを明らかにするとともに、それらのシグナル物質を合成・分解する酵素の遺伝子破壊株を作製し、それらの酵素及びシグナル物質の機能を明らかにすることを目的として研究を行っている。
一方、それらのシグナル物質はATPの合成基質になるという結果が得られてきているので、これらを基質とした飢餓時のATP合成システムについての解明を行っている。
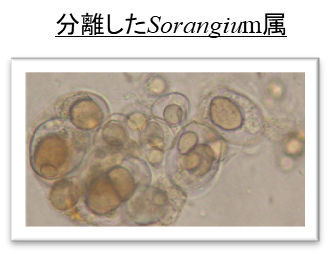
2.Sorangium属の自然界からの分離と有用物質の探索
細菌の中で最も多くの遺伝子を有することから新規な生理活性物質を生産している可能性があるものの、難培養性細菌であるため純化が難しく、日本では分離されていない粘液細菌の分離及び純化方法を確立し、放線菌に替わる新しい微生物資源を構築することを目的として自然界から粘液細菌を分離している。粘液細菌の菌株と培養抽出物のライブラリーを作製することで、企業等の共同研究において創薬のための新規リード化合物の探索を行いたい。

代表的な研究業績
- Kimura, Y. et al. (2017). High concentrations of intracellular Ap4A and/or Ap5A in developing Myxococcus xanthus cells inhibit sporulation. Microbiology 163:86-93.
- Oka, M. et al. (2016). Lysyl-tRNA synthetase from Myxococcus xanthus catalyzes the formation of diadenosine penta- and hexaphosphates from adenosine tetraphosphate. Archieves of Biochemistry and Biophysics. 604:152-158.
- Sasaki, M. et al. (2014). Enzymatic characteristics of an ApaH-like phosphatase, PrpA, and a diadenosine tetraphosphate hydrolase, ApaH, from Myxococcus xanthus enzymes. FEBS Letters 588:3395-3402.
- Kimura, Y. et al. (2012). Function analysis of a bacterial tyrosine kinase, BtkB, in Myxococcus xanthus. FEMS Microbiological Letters 336(1):45-51 (2012).
- Mori, Y. et al. (2012). PhpA, a tyrosine phosphatase of Myxococcus xanthus, is involved in the production of exopoly-saccharide. Microbiology158(10):2546-2555.
- Kimura, Y. et al. (2011). A Myxococcus xanthus bacterial tyrosine kinase, BtkA, is required for the formation of mature spores. Journal of Bacteriology 193(20):5853-5857.
Research Area: Applied Life Science
Research Specialization: MicrobialPhysiology
Name: KIMURA, Yoshio

Keywords: Myxobacteria, signal transduction, ATP synthesis, Novel microbial resources

Recent Research
1. Signal molecules of Myxobacteria.
When environmental conditions become unfavorable,organisms produce signal molecules and can respond to changes in their environment. Diadenosine polyphosphate (ApnA; n=3-6) and polyphosphateare produced during amino acid-starvation. We try to identify and characterize key enzymes involved in these signal molecules of synthesis and degradation. Further, we generate gene-broken strains in which the enzyme genes are broken, and we will clarify the function of these enzymes and signal molecules.
On the other hand, we are revealing that these signal molecules are substrates for ATP synthesis enzymes. We now studying that ATP synthesis system using these signal molecules under amino acid-starvation.
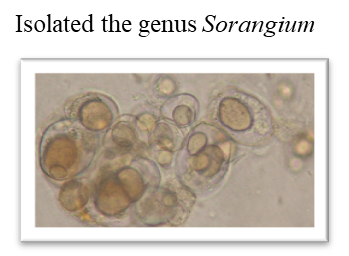
2. Isolation of Sorangium from the natural world andSearch for useful substances.
Gram-negative myxobacteria are an important source of novel classes of secondary metabolites. Of these, the genus Sorangium is particularly valuable. Therefore, we are isolating the genus Sorangium form soil.
Natural products are extracted from Sorangium cultures, and are provided for microbial growth inhibition experiments. In addition, the extracts are analyzed by LC-MS.
we are exploring useful substances from these cultures of Sorangium.

Publications
- Kimura, Y. et al. (2017). High concentrations of intracellular Ap4A and/or Ap5A in developing Myxococcus xanthus cells inhibit sporulation. Microbiology 163:86-93.
- Oka, M. et al. (2016). Lysyl-tRNA synthetase from Myxococcus xanthus catalyzes the formation of diadenosine penta- and hexaphosphates from adenosine tetraphosphate. Archieves of Biochemistry and Biophysics. 604:152-158.
- Sasaki, M. et al. (2014). Enzymatic characteristics of an ApaH-like phosphatase, PrpA, and a diadenosine tetraphosphate hydrolase, ApaH, from Myxococcus xanthus enzymes. FEBS Letters 588:3395-3402.
- Kimura, Y. et al. (2012). Function analysis of a bacterial tyrosine kinase, BtkB, in Myxococcus xanthus. FEMS Microbiological Letters 336(1):45-51 (2012).
- Mori, Y. et al. (2012). PhpA, a tyrosine phosphatase of Myxococcus xanthus, is involved in the production of exopoly-saccharide. Microbiology158(10):2546-2555.
- Kimura, Y. et al. (2011). A Myxococcus xanthus bacterial tyrosine kinase, BtkA, is required for the formation of mature spores. Journal of Bacteriology 193(20):5853-5857.
このページの管理者:管理者