領域名 植物科学
教員氏名 野 村 美 加
研究分野 植物栄養学

研究キーワード:共生,マメ科植物,根粒, 根粒菌, 窒素固定

最近の研究課題
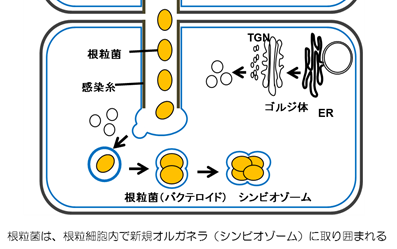
マメ科植物は根粒菌が感染すると、根毛にできる感染糸を通り、皮層細胞へ進入後、根に根粒を形成します。一方、根粒内では根粒菌がバクテロイドへ分化し、植物細胞膜由来のペリバクテロイド膜に取り囲まれます。本研究では、マメ科植物と根粒菌が共生に必要な新規オルガネラ形成に必要なSNAREタンパク質に着目し調べています。近年、SNAREの一つが皮層細胞内の感染糸伸長、シンビオゾーム形成に必要であることを明らかにしました。現在はそのSNAREと複合体を形成するタンパク質を調べています。

2.共生窒素固定を調節する転写因子の解析
根粒菌が根粒内で共生窒素固定を行うためには植物地上部から炭素源を供給されなければなりません。これまでに共生に必要な炭素代謝酵素について調べ、PEPC酵素が重要な酵素として機能することを明らかにしています。本研究ではこの炭素代謝酵素の転写因子を明らかにして根粒内の炭素による制御機構を明らかにしようと試みています。また、窒素固定により発現する遺伝子群を網羅的に解析を行い、共生窒素固定に必要な転写因子についても調べています。
3 . 根粒老化に関与する遺伝子群の解析
根粒は鉄を大量に蓄積していますが、根粒が老化すると根粒内の鉄含量が低下し、地上部への転流されます。しかし老化時にタンパク質から遊離した鉄イオンは、有害であるため鉄貯蔵タンパク質であるフェリチンに蓄積されます。本研究ではフェリチンタンパク質を介した鉄の再利用に必要な発現機構、輸送系の解明を試みています。


代表的な研究業績
- Iron-induced nitric oxide leads to an increase in the expression of ferritin during the senescence of Lotus japonicus nodules, Chungopast, S., Duangkhet, M., Tajima, S., Ma,J.F., Nomura, M. J Plant Physiol. 208, 40-46 (2017)
- A MYB-related transcription factor affects nodule formation in Lotus japonicus, Supriadi, Duangkhet,M., Thepsukhon, A., Widyastuti, R., Santosa, D.A., Tajima, S., Nomura, M. Plant Biotech. 33, 187-194 (2016)
- Transcriptomic profiles of nodule senescence in Lotus japonicus and Mesorhizobium loti symbiosis, Chungopast, S., Hirakawa, H., Sato, S., Handa, Y., Saito, K., Kawaguchi, M., Tajima, S., Nomura, M. . Plant Biotech, 31, 345-349 (2014)
- Glutamine synthetase I-deficiency in Mesorhizobium loti differentially affects nodule development and activity in Lotus japonicus, Chungopast, S., Thapanapongworakul, P., Matsuura, H., Dao, T.V., Asahi, T., Tada, K., Tajima, S., and Nomura, M. J Plant Physiol., 171, 104-108 (2014)
Research Area: Plant Science
Research Specialization: Molecular Plant Nutrition
Name: NOMURA, Mika

Keywords:symbiosis,legume, nodule,nitrogen fixation

Recent Research
1. Membrane fusion by SNARE in Lotus japonicus nodule
Legume produces nodules when rhizobia infect with root and fixes atmospheric nitrogen to produce ammonia. In the nodule these rhizobia are enclosed by plant derived organelles, symbiosome, and differentiate into the bacteroid.
We are studying the SNARE protein which has function for the nodule formation and could find one of the SNAREs which has important role to produce symbiosome in Lotus nodules. We are now analyzing for the SNARE complex proteins for the symbiosome membrane.

2. Transcription factors for the nitrogen fixation
When rhizobia fix nitrogen in the nodule, legume has to provide carbon source. We have previously found that PEPC which expresses in the nodule for the production of respiratory substrate, malate (Nomura et al, PCP 2006). However, there is no report of the transcription factors for the regulation of carbon metabolism in the nodule. We are now analyzing for the transcription factors for the regulation of nitrogen fixation.

3. Analysis of ferritin for the nodule senescence
We have performed the transcriptome analysis for the nodule senescence and found that an iron accumulating protein, ferritin, accumulates in the aging nodule (Cungopast et al., Plant Biotech, 2014, J Plant Physiol, 2017). We speculates these iron would be transported to shoot. We are analyzing iron transporter in the nodule.

Click here for more information.

Publications
- Iron-induced nitric oxide leads to an increase in the expression of ferritin during the senescence of Lotus japonicus nodules, Chungopast, S., Duangkhet, M., Tajima, S., Ma,J.F., Nomura, M. J Plant Physiol. 208, 40-46 (2017)
- A MYB-related transcription factor affects nodule formation in Lotus japonicus, Supriadi, Duangkhet,M., Thepsukhon, A., Widyastuti, R., Santosa, D.A., Tajima, S., Nomura, M. Plant Biotech. 33, 187-194 (2016)
- Transcriptomic profiles of nodule senescence in Lotus japonicus and Mesorhizobium loti symbiosis, Chungopast, S., Hirakawa, H., Sato, S., Handa, Y., Saito, K., Kawaguchi, M., Tajima, S., Nomura, M. . Plant Biotech, 31, 345-349 (2014)
- Glutamine synthetase I-deficiency in Mesorhizobium loti differentially affects nodule development and activity in Lotus japonicus, Chungopast, S., Thapanapongworakul, P., Matsuura, H., Dao, T.V., Asahi, T., Tada, K., Tajima, S., and Nomura, M. J Plant Physiol., 171, 104-108 (2014)
このページの管理者:管理者