領 域 名 植物科学
教員氏名 市村 和也
研究分野 植物ゲノム機能解析学

研究キーワード: 植物免疫,環境ストレス,シグナル伝達,青枯病菌,エフェクター,シロイヌナズナ,ベンサミアナタバコ

1.MAPキナーゼ経路を介した植物免疫シグナル伝達機構
1.1 MEKK1→MKK1/MKK2→MPK4経路欠損による防御反応表現型の解析
本研究室では、植物免疫シグナル伝達の分子機構を解明するため、MAMPs (微生物分子パターン)により活性化するシロイヌナズナMAPキナーゼ経路の1つ、MEKK1(MAPKKK) → MKK1/MKK2 (MAPKKs) → MPK4(MAPK) 経路について研究を行っている。本経路の活性化は基礎免疫であるパター誘導免疫における防御反応を正に制御すると考えられているが、経路構成因子の欠損は細胞死を始めとするエフェクター誘導免疫様防御反応を構成的に示す。この一見矛盾する現象の背後にある複雑な制御機構を明らかにするため、シロイヌナズナゲノム情報を駆使して遺伝学的、分子生物学的な解析手法を取りながら研究を進めている。
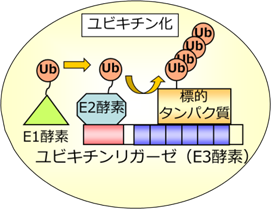
1.2 MEKK1→MKK1/MKK2→MPK4経路の制御に関係するユビキチンリガーゼの機能
我々の研究室では、上記MAPキナーゼ経路の研究を進める過程で、最上流因子であるMEKK1の制御因子を同定するため、MEKK1結合タンパク質の探索を行った。その結果、ユビキチンリガーゼを単離した。単離されたユビキチンリガーゼが、MEKK1以下の経路に対してどのような機能を果たしているのか、変異体などを用いて分子生物学的に研究を行っている。

1.3 タンパク質間相互作用に基づいた新たなシロイヌナズナMAPキナーゼ経路の同定
シロイヌナズナゲノムでは、80以上のMAPKKK遺伝子、10個のMAPKK遺伝子、20個のMAPK遺伝子が存在することが明らかになっている。このことから、様々な組み合わせでMAPキナーゼ経路が構成され、種々の細胞外シグナルを細胞内に伝達していることが推測される。本研究室では、シロイヌナズナMAPキナーゼ経路について、網羅的なタンパク質結合検定を行い、新奇なMAPキナーゼ経路の同定を進めている。
2.新たな植物免疫シグナル伝達機構同定に向けた青枯病菌 functional effectomics
青枯病菌 (Ralstonia solanacearum)はナス科植物を中心に200種類以上の植物に対して青枯病を引き起こす植物病原細菌である。青枯病菌の広い宿主範囲は、病原性細菌として非常に多い(>70)病原性因子であるエフェクターに起因すると考えられている。本研究では青枯病菌エフェクターをツールとして、エフェクターが抑制する植物の標的因子を同定し、新たな植物免疫シグナル伝達機構の同定を目指して解析を進めている。
代表的な研究業績

Ichimura, K. et al., SGT1 contributes to maintaining protein levels of MEK2DD to facilitate hypersensitive response-like cell death in Nicotiana benthamiana, Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology, 94, 47-52, 2016.
Yamada, K. et al., The Arabidopsis CERK1‐associated kinase PBL27 connects chitin perception to MAPK activation, EMBO Journal, 35, 2468-2483, 2016.
Nakamura, S. et al., Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Kinase 3 Regulates Seed Dormancy in Barley, Current Biology, 26, 775-781, 2016.
Stegmann, M. et al. (2012) The ubiquitin ligase PUB22 targets a subunit of the exocyst complex required for PAMP-triggered responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell, 24, 4703-4716.
Takahashi, F. et al. (2011) Calmodulin-dependent activation of MAP kinase for ROS homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Molecular Cell, 41, 649-660.
Research Area: Plant Science
Research Specialization: Plant Functional Genomics and Plant immunity
Name: ICHIMURA, Kazuya

Keywords: Plant immunity, Environmental stress, signal transduction, Ralstonia solanacearum, effector, Arabidopsis thaliana, Nicotiana benthamiana

1. Plant immunity signaling mediated by MAP kinase pathways
1.1 Autoimmunity phenotype of MEKK1 → MKK1 / MKK2 → MPK4 pathway mutants.
Arabidopsis MEKK1, a MAPKKK, comprises specific MAPK pathway with downstream MKK1/MKK2 (MAPKKs) and MPK4 (MAPK). This pathway is activated in the downstream of PRRs and proposed to be involved in a part of PTI signaling. In contrast, loss-of-function of the pathway results in severe dwarfism and constitutive ETI responses such as cell death and ROS accumulation. To elucidate complex mechanism underlying the phenotype, we use genetic and molecular biological approaches using Arabidopsis thaliana genome resources.

1.2 Ubiquitin ligase involved in regulation of MEKK1 → MKK1/MKK2 → MPK4 pathway
We identified a ubiquitin E3 ligase as a MEKK1-binding protein by yeast two-hybrid screening. Molecular biological analyses are in progress to clarify function of E3 ligase in immunity signaling through the MEKK1→ MKK1/MKK2 → MPK4 pathway

1.3 Identification of novel pathway related to an innate immunity singling in Arabidopsis
According to the annotation, Arabidopsis genome contains over 80 MAPKKKs, 10 MAPKKs, and 20 MAPKs. This suggests that the MAP kinase pathways have to be composed of numerous combinations of protein kinases and that transduce various extracellular stimuli to activate physiological responses. We performed binding assay for the Arabidopsis MAP kinase pathway components towards identification of a novel signaling pathway, and we analyze possible pathway to find out its biological role.
2. Ralstonia functional effectomics towards identifying novel immunity signaling in plants
Ralstonia solanacearum is the causative agent of bacterial wilt disease against more than 200 of plant species mainly Solanaceae. The broad host range of bacterial wilt is thought to be conferred by relatively large effector repertoire (> 70) to other pathogenic bacteria. Using the advantage of Ralstonia effector repertoire, we performed functional screening to find effectors suppress defense responses. With these effectors, we aim to identify a novel immunity signaling components in plants.
Publications

Ichimura, K. et al., SGT1 contributes to maintaining protein levels of MEK2DD to facilitate hypersensitive response-like cell death in Nicotiana benthamiana, Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology, 94, 47-52, 2016.
Yamada, K. et al., The Arabidopsis CERK1‐associated kinase PBL27 connects chitin perception to MAPK activation, EMBO Journal, 35, 2468-2483, 2016.
Nakamura, S. et al., Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Kinase 3 Regulates Seed Dormancy in Barley, Current Biology, 26, 775-781, 2016.
Stegmann, M. et al. (2012) The ubiquitin ligase PUB22 targets a subunit of the exocyst complex required for PAMP-triggered responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell, 24, 4703-4716.
Takahashi, F. et al. (2011) Calmodulin-dependent activation of MAP kinase for ROS homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Molecular Cell, 41, 649-660.
このページの管理者:管理者