領 域 名 生命機能科学
教員氏名 末 吉 紀 行
研究分野 分子細胞生物学

研究キーワード:プロテインキナーゼ、プロテインホスファターゼ、ゼブラフィッシュ

最近の研究課題
1. ゼブラフィッシュの初期発生に関与する タンパク質リン酸化制御分子
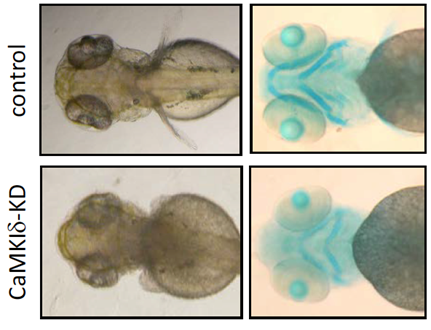
タンパク質のリン酸化は、細胞内情報伝達経路においてタンパク質の機能を迅速に調節する重要な機構である。脊椎動物の初期発生過程においても、プロテインキナーゼとプロテインホスファターゼを介して巧妙に制御されていると考えられる。当研究室では、ゼブラフィッシュをモデル動物として用い、初期の形態形成に関与するタンパク質リン酸化制御分子について解析しており、軟骨と胸鰭の形成に関与するプロテインキナーゼCaMKIdや、神経細胞の生存に必須であるプロテインホスファターゼCaMKP-Nなどを見出した。
2.プロテインホスファターゼの活性制御機構
当研究室では、 数あるプロテインホスファターゼの中でも、活性の発現に2価の金属イオンを必要とするPPMファミリーホスファターゼに着目して研究を進めている。特に、CaMキナーゼに特異的に作用するCaMKP/PPM1Fと、その核局在型CaMKP-N/PPM1Eは当研究グループが発見した分子であり、これらに結合して活性を調節するタンパク質の探索や、細胞内プロセシングやリン酸化を介した活性調節機構の解明を進めている。

代表的な研究業績

- Senga and Akizuki et al. High-performance CaMKI: A highly active and stable form of CaMKId produced by high-level soluble expression in Escherichia coli. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 475, 277-282, 2016
- Onouchi et al. Regulation of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase phosphatase (CaMKP/PPM1F) by Protocadherin-gC5(Pcdh-gC5). Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 585, 109-120, 2015
- Senga et al. Expression and gene knockdown of zebrafish Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase Iδ-LL. Arch. Biochem.Biophys. 540, 41-52, 2013
- Sueyoshi et al. Functional processing of nuclear Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase phosphatase (CaMKP-N): evidence for a critical role of proteolytic processing in the regulation of its catalytic activity, subcellular localization and substrate targeting in vivo. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 517, 43-52, 2012
- Senga et al. Knockdown of two splice variants of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase Iδ causes developmental abnormalities in zebrafish, Daniorerio. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 517, 71-82, 2012
- Onouchi et al. Phosphorylation and activation of nuclear Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase phosphatase (CaMKP-N/PPM1E) by Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase I (CaMKI). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 422, 703-709, 2012
- Baba et al. Regulation of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase phosphatase (CaMKP) by oxidation/reduction at Cys-359. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 526, 9-15, 2012
Research Area: Life Science & Biotechnology
Research Specialization: Molecular and Cellular Biology
Name: SUEYOSHI, Noriyuki

KeyWords:Protein Kinase, Protein Phosphatase, Zebrafish

Recent Research
1. Functions of protein kinases and phosphatases on zebrafish embryogenesis.
Protein kinases and phosphatases are known to play pivotal roles in various signaling pathways and to participate in diverse cellular processes including proliferation, development and differentiation. To investigate protein kinases and phosphatases involved in the developmental processes in zebrafish embryogenesis, we are performing functional gene knockdown experiments in zebrafish using antisense morpholino-modified oligonucleotides that is targeted to the 5’-noncoding sequences of various protein kinases and phosphatases.

2.Regulation of PPM family protein phosphatases.
Ca2+/CaM-dependent protein kinase phosphatase (CaMKP) is a Ser/Thr protein phosphatase that belongs to the PPM family. In our laboratory, we focus on the regulation mechanisms of PPM family phosphatases, especially of CaMKP and CaMKP-N, a nuclear isoform of CaMKP.

Publications

- Senga and Akizuki et al. High-performance CaMKI: A highly active and stable form of CaMKId produced by high-level soluble expression in Escherichia coli. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 475, 277-282, 2016
- Onouchi et al. Regulation of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase phosphatase (CaMKP/PPM1F) by Protocadherin-gC5(Pcdh-gC5). Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 585, 109-120, 2015
- Senga et al. Expression and gene knockdown of zebrafish Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase Iδ-LL. Arch. Biochem.Biophys. 540, 41-52, 2013
- Sueyoshi et al. Functional processing of nuclear Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase phosphatase (CaMKP-N): evidence for a critical role of proteolytic processing in the regulation of its catalytic activity, subcellular localization and substrate targeting in vivo. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 517, 43-52, 2012
- Senga et al. Knockdown of two splice variants of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase Iδ causes developmental abnormalities in zebrafish, Daniorerio. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 517, 71-82, 2012
- Onouchi et al. Phosphorylation and activation of nuclear Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase phosphatase (CaMKP-N/PPM1E) by Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase I (CaMKI). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 422, 703-709, 2012
- Baba et al. Regulation of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase phosphatase (CaMKP) by oxidation/reduction at Cys-359. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 526, 9-15, 2012
このページの管理者:管理者