領 域 名 植物科学
研究分野 植物分子育種学
教員氏名 杉 田 (小 西) 左 江 子

研究キーワード:イネ,脱粒性,画像解析, 多用途米, 品種改良

最近の研究課題
1. イネの脱粒性における離層の形成と崩壊の分子機構の解明
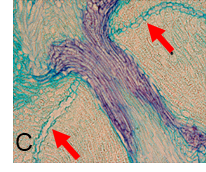
脱粒性とは、穂から種子が脱粒する性質(図A)であり、自然界では種子の拡散による繁殖戦略として重要な性質である。一方、作物として考えた場合、強い脱粒性は収穫量の減少につながるため、今日でも重要な農業形質の1つである。これまでに、当研究室では、イネの脱粒性遺伝子qSH1を単離し、離層形成に必須であることを明らかにしている(図B,C)。また、脱粒性遺伝子qSH1の準同質遺伝子系統NIL(qSH1)を用いて、レーザーマイクロダイセクション法を利用した離層部位特異的なマイクロアレイ解析を行い、qSH1の下流の候補遺伝子を見いだした。現在は、これまでに当研究室で同定したイネ脱粒性遺伝子qSH1および下流の遺伝子、そして、野生イネ由来のsh4遺伝子の3つの遺伝子の相互作用解析を行い、脱粒性における各遺伝子の役割の解明を目指している。さらに、ガンマ線照射を用いた突然変異系統を解析することで、新規遺伝子の探索を進めている。

2. 画像解析を用いたイネの葉の特徴抽
植物の初期生育において、光合成によって得られた化学エネルギーは、まず呼吸等により、植物体(植物細胞)自体の生命活動の維持に消費され、その余剰分が新しい植物体(葉や茎)の形成・生長に使われる。そして、新たに形成された葉もまた光合成を行い、さらなる個体生長に資する。このように初期生育は複雑なポジティブ・フィードバックの様相を呈する。そのため、初期成長時の自然環境のわずかな差異が個体サイズの大きな差につながることがある。当研究室では、自然環境下での植物の個体生長(生長率、生長速度)を非破壊的にモニタリングする測定系(図D,E)を用い、作物であるイネを材料とし、光合成能力の向上そのものではなく、植物生長率の向上を指標にした高CO2吸収イネ系統の作出を目指している。
3. 米粉用イネ品種の選定と応用への模索
近年の小麦価格の急騰の中、イネの米粉としての利用により、食料自給率の向上、耕作放棄地の解消の効果が期待されはじめている。しかしながら、小麦粉と米粉では、アミロース含量、タンパク質含量等、さまざまな成分の差があるため、各用途に応じた品種の開発、利用が必須となる。そこで、米粉を利用する食品に適したイネの品種の選定、特性評価を行っている。


代表的な研究業績

特許(2014):sh4遺伝子を含む、植物体の穀粒サイズを増大させた植物体、特許第5610440号
Nao Tada, Katsuyuki Nii, Saeko Konishi-Sugita (2015) Mutant breeding of a Japanese traditional black rice cultivar ‘Yayoi Murasaki’to improve seed shattering trait,The Nucleus, 58(3):217-223.
Konishi, S. et al. (2008) Inference of japonica rice domestication process from the distribution of six functional nucleotide polymorphisms of domestication-related genes in various landraces and modern cultivers. Plant & Cell Physiology, 49(9), 1283-1293.
Konishi, S. et al. (2006) An SNP caused loss of seed shattering during rice domestication. Science, 312, 1392-1396.
Research Area: Plant Science
Research Specialization: Molecular Breeding in Plant
Name: KONISHI-SUGITA Saeko

Keywords: rice, seed shattering, imaging, breeding

Recent Research
1.Analysis of molecular mechanism about abscission layer formation and degradation in seed shattering in rice
Seed shattering is a trait of seed shedding from panicles (Fig.A). It is an important trait as a breeding strategy by the spread of seeds in nature. On the other hand, when considered as crops, strong seed shattering leads to a reduction in crop yield. Therefore, it is considered to be one of important agricultural traits even today. Our laboratory has isolated seed shatteirng gene qSH1 in rice and it is clear that it is essential for abscission layer formation (Fig.B,C) In addition, a candidate gene downstream of qSH1 was found by performing a site-specific microarray analysis using the laser microdissection method. Furthermore, we are searching for new genes by analyzing mutant strains using gamma ray irradiation.

2. Characteristics extraction of leaves in rice using image analysis
In the early growth of plants, chemical energy obtained by photosynthesis is consumed to maintain life activities of plants by respiration and the like. The surplus is used for the formation and growth of new plants. Newly formed leaves will also photosynthesize and contribute to further individual growth. In this way, initial growth exhibits a complex positive feedback aspect. Therefore, slight differences in the natural environment during initial growth can lead to large differences in individual size. In our laboratory, we used a measurement system (Fig. D, E) for nondestructively monitoring plant growth (growth rate) of plants under natural environment. We are aiming at the production of high CO2-absorbing rice lines with rice as a crop material as an indicator of improvement of plant growth rate.


3. Selection of rice variety for rice flour and challenge to application
In recent years the price of wheat has soared, the use of rice as rice flour, improvement of food self-sufficiency rate, effect of eliminating cultivation abandonment area is beginning to be expected. However, since wheat flour and rice flour have various components such as amylose content and protein content, it is essential to develop and use varieties corresponding to each application. Therefore, selection and characterization of rice varieties suitable for foods using rice flour are being conducted.

Publications

Nao Tada, Katsuyuki Nii, Saeko Konishi-Sugita (2015) Mutant breeding of a Japanese traditional black rice cultivar ‘Yayoi Murasaki’to improve seed shattering trait,The Nucleus, 58(3):217-223.
Konishi, S. et al. (2008) Inference of japonica rice domestication process from the distribution of six functional nucleotide polymorphisms of domestication-related genes in various landraces and modern cultivers. Plant & Cell Physiology, 49(9), 1283-1293.
Konishi, S. et al. (2006) An SNP caused loss of seed shattering during rice domestication. Science, 312, 1392-1396.
このページの管理者:管理者