領 域 名 食品科学
教員氏名 米倉 リナ
研究分野 食品機能化学

研究キーワード: 消化,吸収,機能性物質,ポリフェノール,カロテノイド

最近の研究課題
1. オリーブ果実の抗アレルギー活性成分の効果的機能発現のためのオリーブ製品の開発
オリーブ果実に含まれているポリフェノールのoleuropein aglycone (3,4-DHPEA-EA及び3,4-DHPEA-EDA)による1型アレルギー反応抑制活性が解明され、日本及び世界各国で罹患率が上昇するアトピー性皮膚炎,花粉及び食品アレルギーの発症及び対症療法に役立つ可能性がある.しかし,これらの成分はオリーブオイルには少なく,オリーブ果実では塩漬けに加工する際,水酸化ナトリウム処理(渋抜き)の過程で分解される.すなわち,現在oleuropein aglyconeを効果的に摂取できるオリーブ食品はなく,本研究ではテーブルオリーブのoleuropein aglycone安定性向上を突き止め,新しい加工法の開発を進めている.

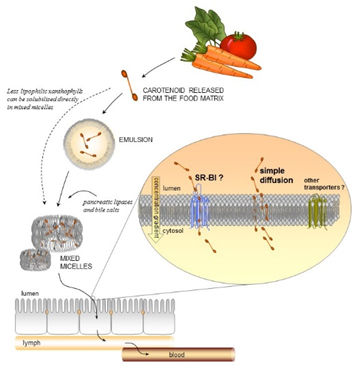
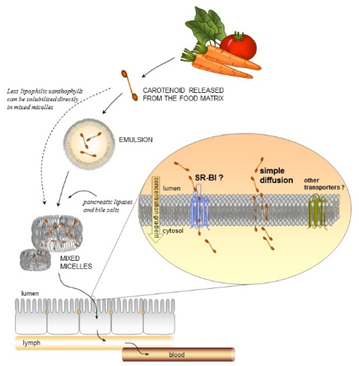
2.カロテノイド類の消化・吸収
カロテノイドは動植物に広く分布している黄~赤の脂溶性色素である。プロビタミンA活性の他,ラジカル捕捉,一重酸素消去,光吸収の生理活性を持つカロテノイドは,がんや加齢性網膜黄斑変性病,血管系疾患,紫外線による皮膚障害などの予防に効果的であると報告されている.食事で摂取するカロテノイドは約60種類あるが,ヒト血漿で検出されるカロテノイドやその代謝物は約10-20に過ぎない.油脂類と比べてカロテノイド類の吸収は非常に低く,本研究室ではカロテノイドの消化・吸収に関わる様々な食事因子についての研究を行っている.
代表的な研究業績

- Soukoulis C, Tsevdou M, Yonekura L, et al. (2017). Does kappa-carrageenan thermoreversible gelation affect β-carotene oxidative degradation and bioaccessibility in o/w emulsions? Carbohydrate Polymers 167, 259-269.
- Yonekura L, Martins CA., Sampaio G, et al. (2016). Bioavailability of catechins from guarana (Paullinia cupana) and its effect on antioxidant enzymes and other oxidative stress markers in healthy human subjects. Food & Function 7, 2970-2978.
- Kano S., Komada H, Yonekura L, Sato A, Nishiwaki, H., and Tamura, H. (2016). Absorption, Metabolism, and Excretion by Freely Moving Rats of 3,4-DHPEA-EDA and Related Polyphenols from Olive Fruits (Olea europaea). Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism 2016, 10.
- Kotake-Nara E, Yonekura L, and Nagao A. (2015). Glyceroglycolipids Affect Uptake of Carotenoids Solubilized in Mixed Micelles by Human Intestinal Caco-2 Cells. Lipids 50, 847-860.
- Yonekura L, et al. (2016). Vitamina A (retinol) e carotenoides In Biodisponibilidade de Nutrientes (5a EDIÇÃO revisada e atualizada), S.M.F. Cozzolino, ed. (Barueri: Manole), pp. 293-340.
Division Food Sciences
Research Field Food chemistry and functionality
Name YONEKURA, Lina

Keywords: Digestion, absorption, bioactive compounds, polyphenols, carotenoids

Recent research topics
Table olive processing methods for preservation of bioactive compounds
Kagawa prefecture is the largest producer of olives in Japan.
Olive fruits contain important bioactive compounds such as the oleuropein aglycones 3,4-DHPEA-EA and 3,4-DHPEA-EA, which have strong antiallergic effects in addition to their antioxidant properties. However, most of those bioactive compounds are lost with the intensive chemical treatment and rinsing during the process to make table olives. We are studying methods to improve the stability of bioactives in table olives, while reducing the environmental impact of the process by reducing the use of water.

Digestion and absorption of carotenoids and polyphenols
Carotenoids and polyphenols are important food bioactives. Carotenoids are red, orange and yellow pigments that are radical scavengers, antioxidants and have an important role in the prevention of cancer, and age-related macular degeneration. Catechins are also important modulators of the body’s redox status.
Carotenoids are poorly absorbed. Only 10-20% of the ingested amount is actually absorbed. The bioavailability of catechins is even lower. We are investigating the effect of dietary factors that can improve the absorption of carotenoids and catechins.
Selected publications

- Soukoulis C, Tsevdou M, Yonekura L, et al. (2017). Does kappa-carrageenan thermoreversible gelation affect β-carotene oxidative degradation and bioaccessibility in o/w emulsions? Carbohydrate Polymers 167, 259-269.
- Yonekura L, Martins CA, et al. (2016). Bioavailability of catechins from guarana (Paullinia cupana) and its effect on antioxidant enzymes and other oxidative stress markers in healthy human subjects. Food & Function 7, 2970-2978.
- Kano S., Komada H, Yonekura L, et al. (2016). Absorption, Metabolism, and Excretion by Freely Moving Rats of 3,4-DHPEA-EDA and Related Polyphenols from Olive Fruits (Olea europaea). Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism 2016, 10.
- Kotake-Nara E, Yonekura L, and Nagao A. (2015). Glyceroglycolipids Affect Uptake of Carotenoids Solubilized in Mixed Micelles by Human Intestinal Caco-2 Cells. Lipids 50, 847-860.
- Yonekura L, et al. (2016). Vitamina A (retinol) e carotenoides In Biodisponibilidade de Nutrientes (5a EDIÇÃO revisada e atualizada), S.M.F. Cozzolino, ed. (Barueri: Manole), pp. 293-340.
このページの管理者:管理者