領 域 名 生命機能科学
教員氏名 渡 邉 彰
研究分野 微生物生化学

研究キーワード:微生物, 担子菌, キノコ, 酵素, タンパク質, 遺伝子,オートファジー

最近の研究課題
1.キノコが示す生物学的特徴の解析と応用
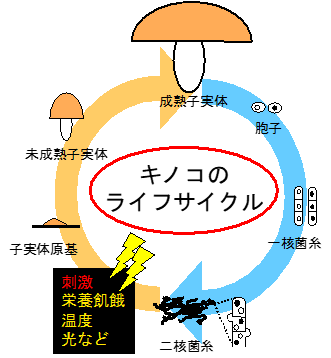
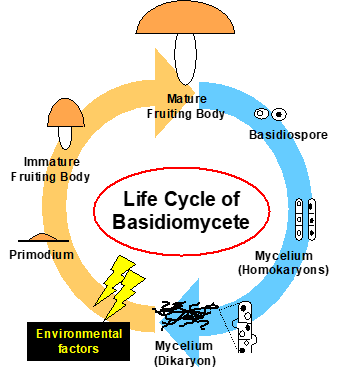
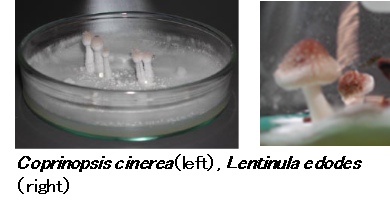
キノコとは、大型の生殖器官(子実体、いわゆるキノコ)を作る真菌類のことであり、その大部分が担子菌に属しています。キノコ(担子菌)は、通常、菌糸状態で生育していますが、栄養飢餓や温度や光などの刺激が加わることにより、菌糸が集合し子実体を形成します(右図参照)。また、キノコには、食用として重要な種や、抗腫瘍性物質などの種々の有用生理活性物質を生産する種が存在するだけでなく、他生物では分解が困難な難分解性高分子化合物を分解する種も存在することから、生産面の他、バイオマス資源の活用面や環境の浄化面においても、その応用が期待されています。
本研究室では、このようなキノコが示す生物学的特徴の解析とその応用を目指し研究に取り組んでいます。
2.キノコのオートファジーに関する研究
オートファジーとは、真核生物におけるタンパク質分解機構の一つであり、オルガネラやタンパク質を包み込む膜を介した大規模な分解系であります。近年、各種真核生物における解析から,オートファジーが栄養飢餓に対する適応だけでなく、細胞分化、細胞内浄化やオルガネラの代謝など、様々な生命現象に関与することが明らかとなってきました。
本研究室では、ユニークな生物学的特徴を保持するキノコ(担子菌)のオートファジーについて、分子生物学および細胞生物学の面から解析を進めています。


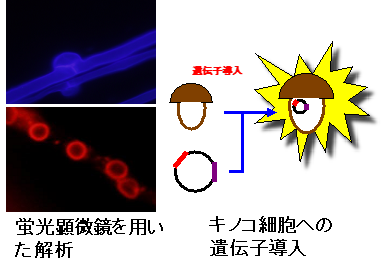
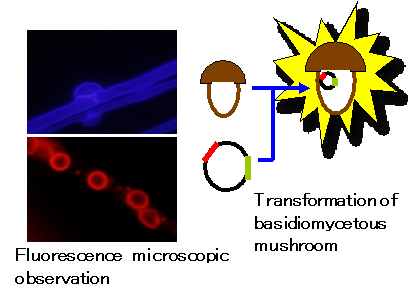
3.キノコの生命現象を解析する分子生物学的ツールの開発
キノコの示すユニークな生命現象を遺伝子・タンパク質レベルで解析するため、本研究室では、キノコにおける効率的な分子生物学ツールの開発も行っています。
代表的な研究業績

- Cesur, A. et al. (2022) Relationship between fruiting body development and extracellular laccase production in the edible mushroom Flammulinavelutipes, Biochemistry and Biophysics Reports, 29: 101204.
- Nitheranont , T. et al. (2018) Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding a major laccase isozyme from Grifolafrondosaand its expression in Pichia pastoris, Mushroom Science and Biotechnology, 25: 134-140.
- Nitheranont , T. et al. (2017) Heterologous expression of two minor laccase isozyme cDNAs from the edible mushroom Grifola frondosa , Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 81: 2367-2369.
- Chairin, T. et al. (2014) Purification and characterization of the extracellular laccase produced by Trametespolyzona WR710-1 under solid state fermentation, Journal of Basic Microbiology 54: 35-43.
Research Area: Applied Life Science
Research Specialization: Microbial Biochemistry
Name: WATANABE, Akira

Keywords: Microorganism, Basidiomycetous mushroom, Enzyme, Protein, Gene, Autophagy

Recent Research
1. Studies on biological characteristics in basidiomycetous mushroom
Basidiomyctes develop a fruiting body (called mushroom) as a large organ that produces many basidiospores (right figures). Fruiting body is formed from the aggregation of mycelia by proper environmental factors. However molecular mechanisms of fruiting body development in basidiomycetes are still unclear. In addition, basidiomycetes are very useful species for application. Because, they include edible, medicinal, and wood-degrading species.
In this laboratory, we study the biological characteristics of basidiomycteous mushrooms.
2. Studies on autophagy of basidiomycetousmushroom
Autophagy is a conserved intercellular degradation system in eukaryotes, which mediates the turnover of cytoplasmic proteins. Recent studies indicate that autophagy is involved not only in response to nutritional starvation but also in various biological phenomena such as cell developmental processes, intracellular clearance and organelle metabolism.
In this laboratory, we study the physiological role of autophagy in basidiomycetous mushroom.

3. Development of molecular biological tools in basidiomycetous mushroom
WWe also attempt to develop the efficient molecular tools (the gene / protein level) of basidiomycetous mushroom.
Publications

- Cesur, A. et al. (2022) Relationship between fruiting body development and extracellular laccase production in the edible mushroom Flammulinavelutipes, Biochemistry and Biophysics Reports, 29: 101204.
- Nitheranont , T. et al. (2018) Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding a major laccase isozyme from Grifolafrondosaand its expression in Pichia pastoris, Mushroom Science and Biotechnology, 25: 134-140.
- Nitheranont , T. et al. (2017) Heterologous expression of two minor laccase isozyme cDNAs from the edible mushroom Grifola frondosa , Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 81: 2367-2369.
- Chairin, T. et al. (2014) Purification and characterization of the extracellular laccase produced by Trametespolyzona WR710-1 under solid state fermentation, Journal of Basic Microbiology 54: 35-43.
このページの管理者:管理者