領 域 名 食品科学
教員氏名 石井 統也
研究分野 食品加工学

研究キーワード:乳化物,泡沫,ゲル,粉末,ミクロゲル,オイルボディ

最近の研究課題
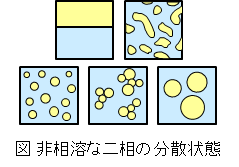
食品の多くは、互いに混ざり合わない複数の相で構成された分散系である(例:水中に油滴が分散した乳化物、水中に気泡が分散した泡沫)。食品中の相の分散状態は、見た目やおいしさといった品質と密接に関わっており、分散状態を適切に制御、維持することが求められる。当研究室では、様々な食品素材や加工処理を駆使し、分散系食品の品質を向上させるための研究を行っている。また、持続可能な食料生産の構築を目指し、新たな植物素材の探索と加工特性の評価を行っている。
1.微粒子による分散系の形成と安定化に関する研究
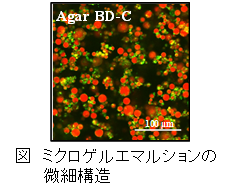
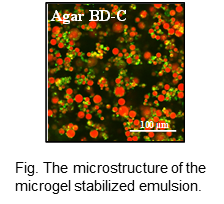
通常、乳化物や泡沫は、タンパク質や界面活性剤など界面活性を有する分子を用いて形成、安定化される。その一方で、分子よりも大きな微粒子も油水界面や気液界面に吸着し、分散系の形成と安定化に寄与することが知られている。当研究室では、野菜や果実の粉末、微小なゲル粒子(ミクロゲル)の乳化特性について研究を行っている。また、ミクロゲルをパンや麺に加えた場合の、テクスチャーへの影響についても解析を試みている。
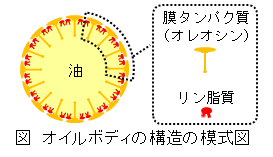
2.植物オイルボディの食品加工特性に関する研究
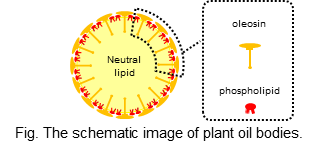
植物中の中性脂質は、膜タンパク質やリン脂質に覆われた、オイルボディと呼ばれる微小な粒子として蓄えられる。当研究室では、これまで、オイルボディと卵黄リポタンパク質との類似性に着目し、オイルボディが優れた乳化特性を有することを明らかにしてきた。このほか、泡沫系への応用、加熱などの加工処理への耐性についても研究を進めている。
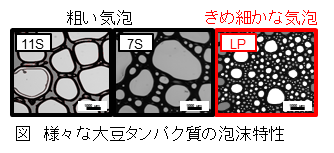
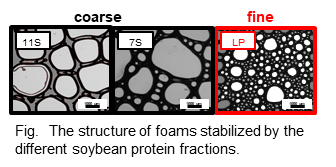
また、大豆油製造の副産物である脱脂大豆から分画される脂質親和性タンパク質(LP)は、 オイルボディに由来する膜タンパク質やリン脂質などで構成されていると考えられている。現在は、LPの乳化特性や起泡特性についても評価を行っている。
代表的な研究業績

- H. Ho, T. Ishii, K. Matsumiya, M. Iwasa, & Y. Matsumura. Utilization of dried Japanese apricot and avocado fruit powders as an emulsifying agent: The importance of the powder-dispersed phase in emulsification. J Food Eng., 294, 110411,2021.
- J. Sirison, T. Ishii, K. Matsumiya, M. Samoto, M. Kohno, & Y. Matsumura. Comparison of surface and foaming properties of soy lipophilic protein with those of glycinin and β-conglycinin. Food Hydrocoll., 112, 106345, 2021.
- T. Ishii, K. Matsumiya, & Y. Matsumura. Combinational effects of acid and salt addition on colloidal, interfacial, and emulsifying properties of purified soybean oil bodies. Food Hydrocoll., 111, 106213, 2021.
- T. Ishii, K. Matsumiya, M. Aoshima, & Y. Matsumura. Microgelation imparts emulsifying ability to surface-inactive polysaccharides—bottom-up vs top-down approaches, NPJ Sci. Food, 2, 15, 2018.
- T. Ishii, K. Matsumiya, Y. Nambu, M. Samoto, M. Yanagisawa, & Y. Matsumura. Interfacial and emulsifying properties of crude and purified soybean oil bodies, Food Structure, 12, 64–72, 2017.
Research Area: Food Science
Research Specialization: Food Processing
Name: ISHII, Toya

Key word: emulsion, foam, gel, powder, microgel, oil body

Recent Research
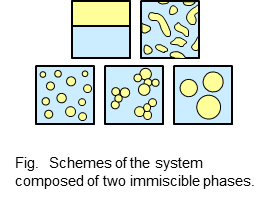
Many food products consist of two or more immiscible phases (e.g., oil and water for emulsions, air and water for foams). The dispersed states of these phases in food stuffs closely relate to the product quality such as appearance and texture. We are studying various food ingredients and processing techniques to control the dispersed states of various food systems for designing the desired product quality. Our another research interest is the assessment and application of plant-based food ingredients towards the sustainable food production.
1. Stabilization of colloidal systems based on edible particles
Food emulsions and foams are usually created and stabilized based on surface-active molecules such as proteins and small-molecule surfactants, whereas recent studies clarified that particles can irreversibly adsorb on oil-water and air-water interface to efficiently stabilize emulsions and foams. We are investigating emulsifying properties of various edible particles, e.g. vegetable powders and microgels.
2. Functions of plant oil bodies (oleosomes) as food ingredients
Plant oil bodies (OBs) are an oil-storing organelle composed of the neutral lipid core, phospholipid monolayer, and oleosin proteins. We are investigating emulsifying and foaming properties of OBs extracted from soybean seeds under various conditions relating to the food processing.
On the other hand, OB-related lipophilic components, e.g., phospholipids and oleosin proteins can be also obtained from defatted soybean meal as a newly-fractionated protein fraction, named soybean lipophilic protein (LP). We are also focusing on the application of LP to food emulsion and foam systems.
Publication

- H. Ho, T. Ishii, K. Matsumiya, M. Iwasa, & Y. Matsumura. Utilization of dried Japanese apricot and avocado fruit powders as an emulsifying agent: The importance of the powder-dispersed phase in emulsification. J Food Eng., 294, 110411, 2021.
- J. Sirison, T. Ishii, K. Matsumiya, M. Samoto, M. Kohno, & Y. Matsumura. Comparison of surface and foaming properties of soy lipophilic protein with those of glycinin and β-conglycinin. Food Hydrocoll., 112, 106345, 2021.
- T. Ishii, K. Matsumiya, & Y. Matsumura. Combinational effects of acid and salt addition on colloidal, interfacial, and emulsifying properties of purified soybean oil bodies. Food Hydrocoll., 111, 106213, 2021.
- T. Ishii, K. Matsumiya, M. Aoshima, & Y. Matsumura. Microgelation imparts emulsifying ability to surface-inactive polysaccharides—bottom-up vs top-down approaches, NPJ Sci. Food, 2, 15, 2018.
- T. Ishii, K. Matsumiya, Y. Nambu, M. Samoto, M. Yanagisawa, & Y. Matsumura. Interfacial and emulsifying properties of crude and purified soybean oil bodies, Food Structure, 12, 64–72, 2017.
このページの管理者:管理者